Economics involves the application of various techniques to enable economic analysis at every stage in the development of oil and gas exploration and production. The economics of any oil and gas project can be affected by a range of factors. Syntillica work with economists who can offer expert economic evaluation, risk analysis and financial modelling.
Economists can generate and develop economic models for oil and gas fields, they can help to establish the economic recoverable reserves and the optimisation of field development plans.
Our consultants can offer a wide range of economic evaluation techniques for projects such as Red Flag Reviews, Due Diligence projects, Decommissioning and end of field economics, through to PRMS compliant Competent Person Reports for stock exchange listing.
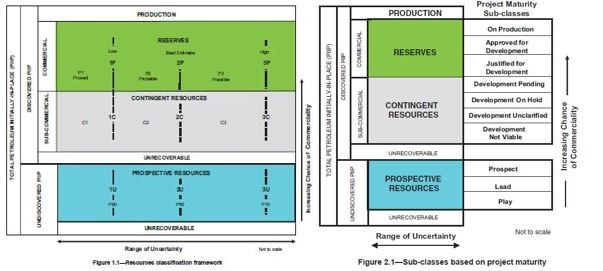
A Competent Person Report (CPR) is a key document in the resources and energy sectors, especially in mining and oil and gas industries. It provides an independent, expert assessment of a company’s mineral or hydrocarbon assets, including their quantity, quality, and economic viability. This report is crucial for investors, stakeholders, and regulatory bodies, as it offers a reliable evaluation of the assets’ value and potential.
Key Aspects of a Competent Person Report (CPR)
1. Purpose and Importance
2. Key Components of a CPR
3. Competent Person’s Qualifications
4. Standards and Guidelines
5. Preparation and Review Process
Conclusion
A Competent Person Report (CPR) is a crucial document in the resource and energy sectors, providing an independent and expert evaluation of a company’s assets. By including detailed resource estimates, economic evaluations, risk analyses, and development plans, the CPR helps investors and stakeholders make informed decisions. Adhering to industry standards and ensuring the independence and expertise of the Competent Person are essential for producing a credible and valuable report.

Project forecasting is a crucial aspect of economic planning and management, involving the estimation of future financial performance and economic outcomes based on current and historical data. In the context of resource and energy projects, such as mining or geothermal energy, accurate forecasting helps stakeholders make informed decisions, manage risks, and allocate resources effectively.
Key Aspects of Project Forecasting
1. Objectives of Project Forecasting
2. Components of Project Forecasting
3. Forecasting Methods and Techniques
4. Challenges and Considerations
5. Best Practices for Effective Forecasting
Conclusion
Project forecasting is a vital process in economic planning, providing valuable insights into future financial performance and resource requirements. By incorporating accurate data, employing robust forecasting methods, and addressing potential challenges, organizations can make informed decisions, manage risks effectively, and optimize project outcomes. Regular updates and transparent methodologies further enhance the reliability and utility of forecasts, supporting successful project execution and investment strategies.

Asset evaluation involves determining the value of assets, which can include tangible assets like property, equipment, and machinery, as well as intangible assets such as intellectual property, brand value, and goodwill. Accurate asset evaluation is essential for various purposes, including financial reporting, investment analysis, mergers and acquisitions, and strategic planning.
Key Aspects of Asset Evaluation
1. Purpose of Asset Evaluation
2. Types of Assets
3. Valuation Methods
4. Factors Influencing Asset Value
5. Challenges in Asset Evaluation
6. Best Practices for Asset Evaluation
Conclusion
Asset evaluation is a critical process that provides valuable insights into the value of various assets, supporting financial planning, investment decisions, and strategic management. By employing appropriate valuation methods, considering influencing factors, and addressing challenges, organizations can achieve accurate and reliable asset evaluations that enhance decision-making and financial outcomes.

Risk review is a critical component of economic management, especially in project planning, investment, and strategic decision-making. It involves identifying, assessing, and managing potential risks that could impact the success of a project or investment. Effective risk review helps organizations anticipate potential challenges, mitigate adverse effects, and make informed decisions.
Key Aspects of Risk Review
1. Objectives of Risk Review
2. Risk Identification
3. Risk Assessment
4. Risk Management Strategies
5. Risk Monitoring and Review
6. Integration with Project and Financial Management
7. Challenges in Risk Review
8. Best Practices for Effective Risk Review
Conclusion
Risk review is a fundamental process in economic and project management, providing valuable insights into potential challenges and uncertainties. By systematically identifying, assessing, and managing risks, organizations can enhance their decision-making, improve project outcomes, and safeguard their investments. Effective risk management involves continuous monitoring, stakeholder engagement, and the application of appropriate strategies to mitigate potential impacts and navigate uncertainties.

Fiscal regimes refer to the policies and frameworks established by governments to manage and regulate the economic interactions between the state and private entities, particularly in the context of resource extraction industries, such as mining, oil and gas, and renewable energy. These regimes are designed to ensure that the government benefits fairly from the extraction of natural resources, while also providing a stable and attractive environment for investment.
Key Components of Fiscal Regimes
Types of Fiscal Regimes
Key Considerations in Designing Fiscal Regimes
Conclusion
Fiscal regimes are critical for managing the economic relationship between governments and private entities in the resource extraction sector. By designing effective fiscal frameworks, governments can ensure a fair distribution of resource revenues, attract investment, and support sustainable development. Balancing the interests of investors with those of the government and local communities is essential for achieving long-term economic and social goals.

Annual auditing is a crucial process in financial management and governance, involving the independent examination of an organization’s financial statements and operations. The objective is to provide assurance on the accuracy, completeness, and reliability of the financial information presented by the organization. This process helps ensure that financial statements are prepared in accordance with accounting standards and regulatory requirements, and it supports transparency and accountability.
Key Aspects of Annual Auditing
1. Purpose of Annual Auditing
2. Types of Audits
3. Audit Process
4. Audit Standards and Regulations
5. Roles and Responsibilities
6. Challenges and Considerations
7. Best Practices for Effective Annual Auditing
Conclusion
Annual auditing is essential for ensuring the accuracy, reliability, and compliance of financial statements and operations. By following established standards and best practices, organizations can achieve greater transparency, enhance stakeholder confidence, and improve overall financial and operational performance. Regular audits provide valuable insights, help detect potential issues, and support effective governance and management.

Investor memoranda, also known as investment memoranda or offering memoranda, are comprehensive documents prepared to inform and attract potential investors. They are used primarily in private equity, venture capital, and mergers and acquisitions to provide detailed information about an investment opportunity. The purpose is to present a compelling case for investment by outlining key aspects of the investment opportunity, including financial projections, business plans, and risk factors.
Key Components of an Investor Memorandum
Purpose and Use of Investor Memoranda
Best Practices for Preparing an Investor Memorandum
Conclusion
An investor memorandum is a vital tool in the investment process, offering detailed insights into an investment opportunity and supporting informed decision-making by potential investors. By presenting a well-rounded and professionally prepared memorandum, companies can effectively communicate the value of their investment opportunities, attract suitable investors, and secure necessary funding.

Defense documents in the context of economics and finance refer to a range of documents and reports used to justify or protect economic or financial decisions, particularly in the context of audits, investigations, and regulatory reviews. These documents can be crucial for businesses and organizations when they need to explain, substantiate, or defend their financial practices, decisions, or performance.
Key Types of Defense Documents
Importance of Defense Documents
Best Practices for Preparing Defense Documents
Conclusion
Defense documents play a critical role in the financial and operational management of organizations, providing necessary support and justification for financial decisions and practices. By maintaining thorough, accurate, and well-organized documentation, organizations can enhance transparency, ensure regulatory compliance, and effectively manage risks and performance.