Syntillica Combines Single Discipline Services for Multi-Disciplinary Synergy Teams.
In addition to the ability to create multi-disciplinary teams, Syntillica maintains a state-of-the-art Project Management Server facilitating the process of planning, co-ordinating, executing and documenting projects.

Peer review is a crucial process to ensure the quality, accuracy, and reliability of technical work. It involves a systematic examination of a project, process, or document by experts in the field who are not directly involved in the work being reviewed. Here’s a detailed overview of the peer review process and its significance in the energy industry:
Objectives of Peer Review
Types of Peer Review
Peer Review Process
Benefits of Peer Review
Challenges in Peer Review
Case Studies
Conclusion
Peer review within the energy industry is a critical component of ensuring high standards of quality, safety, and efficiency. By systematically evaluating technical work through the lens of experienced experts, energy companies can mitigate risks, improve processes, and drive innovation. Despite its challenges, the benefits of peer review make it an indispensable practice in the successful execution of energy projects.

In the energy industry, business services play a vital role in implementing and enhancing Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) initiatives. These services not only support the operational goals of energy companies but also help integrate sustainability and social responsibility into their core business strategies. Here’s an overview of how business services contribute to CSR in the energy sector:
1. Consulting Services
2. Stakeholder Engagement
3. Supply Chain Management
4. Training and Development
5. Data Management and Analytics
6. Innovative Technology Solutions
7. Project Management
8. Corporate Governance and Ethics
9. Health, Safety, and Environment (HSE) Services
10. Partnership Development
Conclusion
Business services in the energy industry are crucial for advancing Corporate Social Responsibility initiatives. By integrating sustainability into their operations and fostering community relationships, energy companies can enhance their reputation, mitigate risks, and contribute positively to society and the environment. Ultimately, effective CSR practices lead to long-term benefits for both the companies and the communities they serve.

Thanks to the wealth of technical and academic expertise from Syntillica’s consultants the company is able to offer bespoke training across the full range of service disciplines:
Training can also be delivered as an integrated collection of technical and management courses to cater for rapid staff development into management positions.
Training is delivered conveniently via common video-conference systems to anywhere with an Internet connection and recorded for future reference.

Management advisory services are designed to enhance organizational performance, streamline operations, and facilitate strategic decision-making. These services focus on providing expert guidance and innovative solutions tailored to the unique challenges and opportunities within the energy sector, encompassing traditional energy sources as well as renewable energy.
Key Areas of Management Advisory Services
Benefits of Management Advisory Services
By leveraging management advisory services, energy companies can effectively navigate the complexities of the industry, drive operational excellence, and achieve strategic objectives. These services provide valuable support across various dimensions, including strategic planning, operational efficiency, financial management, and risk mitigation, empowering organizations to thrive in a dynamic energy landscape.

Strategic consulting services focus on helping organizations navigate complex market dynamics, enhance competitiveness, and achieve sustainable growth. These services encompass a wide range of areas, including market analysis, strategic planning, operational excellence, and risk management, tailored specifically to the unique challenges and opportunities in the energy sector.
Key Areas of Strategic Services
Benefits of Strategic Consulting Services
By leveraging strategic consulting services, energy companies can effectively navigate the complexities of the industry, drive innovation, and achieve their long-term objectives. These services provide essential support across various dimensions, including market analysis, operational efficiency, risk management, and sustainability, empowering organizations to thrive in a dynamic energy landscape.

Competitor analysis is a crucial component of strategic planning in the energy industry, enabling organizations to understand their competitive landscape, identify market trends, and develop strategies to enhance their position in the market. This analysis involves evaluating competitors’ strengths, weaknesses, strategies, and performance, providing valuable insights that inform decision-making and strategic initiatives.
Key Areas of Competitor Analysis Services
Benefits of Competitor Analysis Services
By leveraging competitor analysis services, energy organizations can gain valuable insights into their competitive landscape, enhancing their strategic positioning and overall performance. These services provide essential support in areas such as market assessment, product comparison, pricing strategy, and customer insights, empowering companies to navigate the complexities of the energy sector effectively.

In the highly competitive energy sector, companies must differentiate themselves and maintain a competitive edge to thrive. Business services aimed at enhancing competitive advantage focus on strategic positioning, operational efficiency, innovation, and stakeholder engagement. These services help organizations leverage their strengths, address market challenges, and capitalize on opportunities.
Key Areas of Competitive Advantage Services
Benefits of Competitive Advantage Services
By leveraging competitive advantage services, energy companies can strategically position themselves in the market, enhance operational efficiency, and build strong relationships with stakeholders. These services provide essential support in areas such as market analysis, innovation, customer engagement, and risk management, empowering organizations to thrive in a dynamic and rapidly evolving energy industry.

Change management is a critical discipline, where organizations must continuously adapt to evolving market conditions, technological advancements, regulatory requirements, and environmental challenges. Effective change management ensures that transitions are smooth, minimizing disruption and maximizing the potential for successful outcomes. Business services focused on change management help organizations develop the necessary strategies, processes, and tools to navigate change effectively.
Key Areas of Change Management Services
Benefits of Change Management Services
By leveraging change management services, energy organizations can navigate transitions more effectively, ensuring that they remain competitive and responsive to market dynamics. These services provide critical support in areas such as change strategy development, stakeholder engagement, training, and sustainability, empowering organizations to achieve their change objectives and drive success in the energy sector.
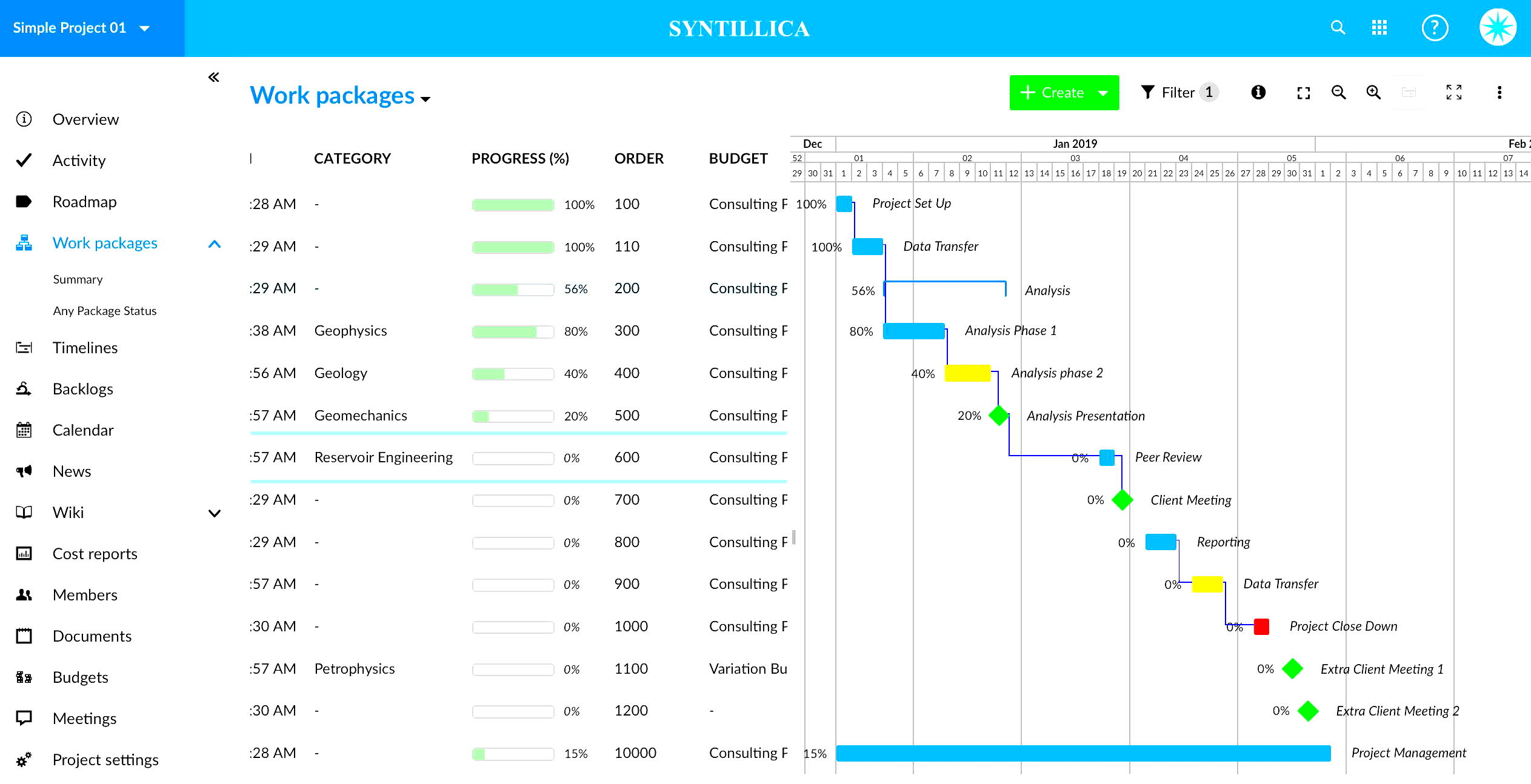
Project management involves a comprehensive approach to planning, executing, and finalizing projects. These projects can range from developing new energy infrastructure to upgrading existing systems, implementing renewable energy technologies, or managing complex maintenance tasks. Here’s an in-depth look at how project management functions:
1. Project Initiation
2. Project Planning
3. Design and Engineering
4. Procurement and Contracting
5. Project Execution
6. Health, Safety, and Environment (HSE) Management
7. Communication and Stakeholder Management
8. Cost Management
9. Project Monitoring and Control
10. Project Closure
Conclusion
Project management within the energy industry is critical for ensuring the successful completion of complex projects. By applying a structured approach to planning, execution, and closure, energy companies can achieve their project goals efficiently, sustainably, and safely. Effective project management helps mitigate risks, manage resources effectively, and deliver high-quality outcomes that meet stakeholder expectations and regulatory requirements.