Appraisal services involve a series of technical and economic evaluations aimed at assessing the viability of an oil or gas field after an initial discovery. These services are crucial for making informed decisions about field development and investment. The appraisal phase bridges the gap between exploration and development, providing critical data that influences the overall strategy for field exploitation.
Key Components of Appraisal Services
- Geological and Geophysical Analysis
- Seismic Surveys and Reprocessing:
- Conducting advanced 3D and 4D seismic surveys to obtain high-resolution subsurface images.
- Reprocessing existing seismic data to improve the accuracy of subsurface models.
- Geological Mapping:
- Detailed geological mapping to define the structure, stratigraphy, and distribution of reservoir rocks.
- Identifying potential drilling hazards and structural traps.
- Seismic Surveys and Reprocessing:
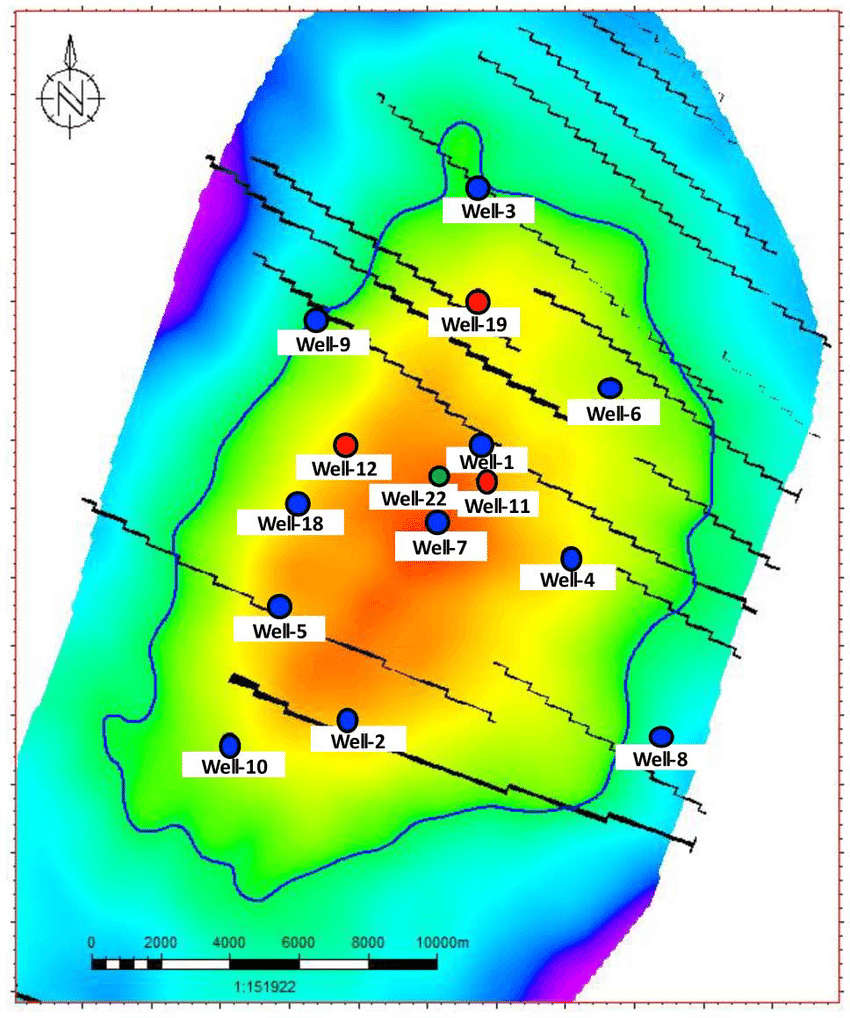
- Reservoir Characterization
- Core Sampling and Analysis:
- Obtaining core samples from exploratory wells to study rock properties such as porosity, permeability, and fluid saturation.
- Conducting laboratory tests on core samples to determine mechanical and petrophysical properties.
- Well Logging:
- Running a suite of well logs (e.g., gamma ray, resistivity, density, and neutron logs) to gather continuous downhole data.
- Integrating log data with core and seismic information to build accurate reservoir models.
- Formation Testing:
- Performing Drill Stem Tests (DSTs) and Modular Formation Dynamics Tests (MDTs) to measure reservoir pressure, temperature, and fluid properties.
- Analyzing pressure transient data to estimate reservoir permeability and boundaries.
- Core Sampling and Analysis:
- Reservoir Modeling and Simulation
- Static Reservoir Modeling:
- Constructing 3D static models to represent the geological features of the reservoir.
- Incorporating seismic, well log, and core data into the model to accurately depict the reservoir structure.
- Dynamic Reservoir Simulation:
- Developing dynamic models to simulate fluid flow within the reservoir.
- Running simulations to predict future production performance under various development scenarios.
- Static Reservoir Modeling:
- Fluid Characterization
- PVT Analysis (Pressure-Volume-Temperature):
- Collecting reservoir fluid samples and conducting PVT analyses to determine fluid properties (e.g., density, viscosity, phase behavior).
- Laboratory Testing:
- Performing laboratory tests on fluid samples to determine compositional characteristics and physical properties.
- Evaluating fluid compatibility with various enhanced recovery methods.
- PVT Analysis (Pressure-Volume-Temperature):
- Drilling and Well Testing
- Appraisal Drilling:
- Planning and executing appraisal wells to gather additional data and confirm reservoir extent.
- Utilizing advanced drilling techniques to minimize formation damage and obtain high-quality data.
- Extended Well Testing (EWT):
- Conducting EWTs to gather long-term production data and assess reservoir behavior.
- Analyzing test results to refine reservoir models and production forecasts.
- Appraisal Drilling:
- Economic Evaluation and Risk Assessment
- Economic Analysis:
- Performing detailed economic evaluations to estimate the potential value of the field.
- Calculating key financial metrics such as Net Present Value (NPV), Internal Rate of Return (IRR), and payback period.
- Risk Assessment and Management:
- Identifying and assessing technical, financial, and operational risks.
- Developing risk mitigation strategies to enhance project viability.
- Economic Analysis:
- Development Planning
- Field Development Scenarios:
- Evaluating multiple development scenarios to identify the optimal approach.
- Considering factors such as well placement, production rates, and recovery methods.
- Infrastructure Requirements:
- Assessing infrastructure needs for surface and subsurface facilities.
- Planning for the installation of production equipment, pipelines, and processing facilities.
- Field Development Scenarios:
- Regulatory and Environmental Compliance
- Permitting and Approvals:
- Identifying and obtaining necessary regulatory permits and approvals for appraisal activities.
- Ensuring compliance with environmental regulations and guidelines.
- Environmental Impact Assessments (EIAs):
- Conducting EIAs to evaluate the potential environmental impact of appraisal and development activities.
- Developing mitigation measures to minimize environmental harm.
- Permitting and Approvals:
- Stakeholder Engagement and Reporting
- Stakeholder Communication:
- Engaging with stakeholders, including regulatory authorities, local communities, and investors.
- Providing transparent and accurate information about appraisal activities and results.
- Reporting and Documentation:
- Preparing comprehensive reports detailing appraisal findings, interpretations, and recommendations.
- Maintaining accurate and organized records for regulatory compliance and future reference.
- Stakeholder Communication:
Benefits of Complete Appraisal Services
- Improved Decision-Making:
- Provides critical data and insights to inform development strategies and investment decisions.
- Enhanced Reservoir Understanding:
- Improves the understanding of reservoir characteristics and behavior, leading to more accurate production forecasts.
- Risk Mitigation:
- Identifies potential risks and develops strategies to mitigate them, enhancing project viability.
- Optimized Development Planning:
- Helps in designing efficient and cost-effective field development plans.
- Regulatory Compliance:
- Ensures adherence to all regulatory requirements, minimizing legal and environmental risks.
- Stakeholder Confidence:
- Builds trust and confidence among stakeholders through transparent communication and responsible management.
By leveraging complete appraisal services, oil and gas companies can make informed decisions about field development, optimize resource recovery, and ensure the economic viability of their projects. These services play a crucial role in bridging the gap between exploration and production, setting the foundation for successful field development and long-term production.